- 2.3 NDB API Classes, Interfaces, and Structures
- 2.3.1 The Column Class
- 2.3.2 The Datafile Class
- 2.3.3 The Dictionary Class
- 2.3.4 The Event Class
- 2.3.5 The Index Class
- 2.3.6 The LogfileGroup Class
- 2.3.7 The List Class
- 2.3.8 The Ndb Class
- 2.3.9 The NdbBlob Class
- 2.3.10 The NdbDictionary Class
- 2.3.11 The NdbEventOperation Class
- 2.3.12 The NdbIndexOperation Class
- 2.3.13 The NdbIndexScanOperation Class
- 2.3.14 The NdbInterpretedCode Class
- 2.3.15 The NdbOperation Class
- 2.3.16 The NdbRecAttr Class
- 2.3.17 The NdbScanFilter Class
- 2.3.18 The NdbScanOperation Class
- 2.3.19 The NdbTransaction Class
- 2.3.20 The Object Class
- 2.3.21 The Table Class
- 2.3.22 The Tablespace Class
- 2.3.23 The Undofile Class
- 2.3.24 The Ndb_cluster_connection Class
- 2.3.25 The NdbRecord Interface
- 2.3.26 The AutoGrowSpecification Structure
- 2.3.27 The Element Structure
- 2.3.28 The GetValueSpec Structure
- 2.3.29 The IndexBound Structure
- 2.3.30 The Key_part_ptr Structure
- 2.3.31 The NdbError Structure
- 2.3.32 The OperationOptions Structure
- 2.3.33 The PartitionSpec Structure
- 2.3.34 The RecordSpecification Structure
- 2.3.35 The ScanOptions Structure
- 2.3.36 The SetValueSpec Structure
Abstract
This section describes the NdbTransaction class
and its public members.
Parent class. None
Child classes. None
Description.
A transaction is represented in the NDB API by an
NdbTransaction object, which belongs to an
Ndb object and is created using
Ndb::startTransaction(). A transaction consists
of a list of operations represented by the
NdbOperation class, or by one of its subclasses
— NdbScanOperation,
NdbIndexOperation, or
NdbIndexScanOperation (see
Section 2.3.15, “The NdbOperation Class”). Each operation access exactly
one table.
Using Transactions.
After obtaining an NdbTransaction object, it is
employed as follows:
-
An operation is allocated to the transaction using one of these methods:
getNdbOperation()getNdbScanOperation()getNdbIndexOperation()getNdbIndexScanOperation()
Calling one of these methods defines the operation. Several operations can be defined on the same
NdbTransactionobject, in which case they are executed in parallel. When all operations are defined, theexecute()method sends them to theNDBkernel for execution. -
The
execute()method returns when theNDBkernel has completed execution of all operations previously defined.Important
All allocated operations should be properly defined before calling the
execute()method. -
execute()performs its task in one of 3 modes, listed here:NdbTransaction::NoCommit: Executes operations without committing them.NdbTransaction::Commit: Executes any remaining operation and then commits the complete transaction.NdbTransaction::Rollback: Rolls back the entire transaction.
execute()is also equipped with an extra error handling parameter, which provides two alternatives:NdbOperation::AbortOnError: Any error causes the transaction to be aborted. This is the default behavior.NdbOperation::AO_IgnoreError: The transaction continues to be executed even if one or more of the operations defined for that transaction fails.
Note
In MySQL 5.1.15 and earlier, these values were
NdbTransaction::AbortOnErrorandNdbTransaction::AO_IgnoreError.
Methods. The following table lists the public methods of this class and the purpose or use of each method:
| Method | Purpose / Use |
|---|---|
getNdbOperation() |
Gets an NdbOperation
|
getNdbScanOperation() |
Gets an NdbScanOperation
|
getNdbIndexScanOperation() |
Gets an NdbIndexScanOperation
|
getNdbIndexOperation() |
Gets an NdbIndexOperation
|
execute |
Executes a transaction |
refresh() |
Keeps a transaction from timing out |
close() |
Closes a transaction |
getGCI() |
Gets a transaction's global checkpoint ID (GCI) |
getTransactionId() |
Gets the transaction ID |
commitStatus() |
Gets the transaction's commit status |
getNdbError() |
Gets the most recent error |
getNdbErrorOperation() |
Gets the most recent operation which caused an error |
getNdbErrorLine() |
Gets the line number where the most recent error occurred |
getNextCompletedOperation() |
Gets operations that have been executed; used for finding errors |
readTuple() |
Read a tuple using NdbRecord
|
insertTuple() |
Insert a tuple using NdbRecord
|
updateTuple() |
Update a tuple using NdbRecord
|
writeTuple() |
Write a tuple using NdbRecord
|
deleteTuple() |
Delete a tuple using NdbRecord
|
scanTable() |
Perform a table scan using NdbRecord
|
scanIndex() |
Perform an index scan using NdbRecord
|
Note
The methods readTuple(),
insertTuple(),
updateTuple(), writeTuple(),
deleteTuple(), scanTable(),
and scanIndex() require the use of
NdbRecord, which is available beginning with
MySQL Cluster NDB 6.2.3.
These methods were updated in MySQL Cluster NDB 6.2.15 and NDB 6.3.15, but remain backward-compatible with their older versions.
For detailed descriptions, signatures, and examples of use for each
of these methods, see Section 2.3.19.2, “NdbTransaction Methods”.
Types.
NdbTransaction defines 3 public types as shown
in the following table:
| Type | Purpose / Use |
|---|---|
AbortOption |
Determines whether failed operations cause a transaction to abort |
CommitStatusType |
Describes the transaction's commit status |
ExecType |
Determines whether the transaction should be committed or rolled back |
For a discussion of each of these types, along with its possible
values, see Section 2.3.19.1, “NdbTransaction Types”.
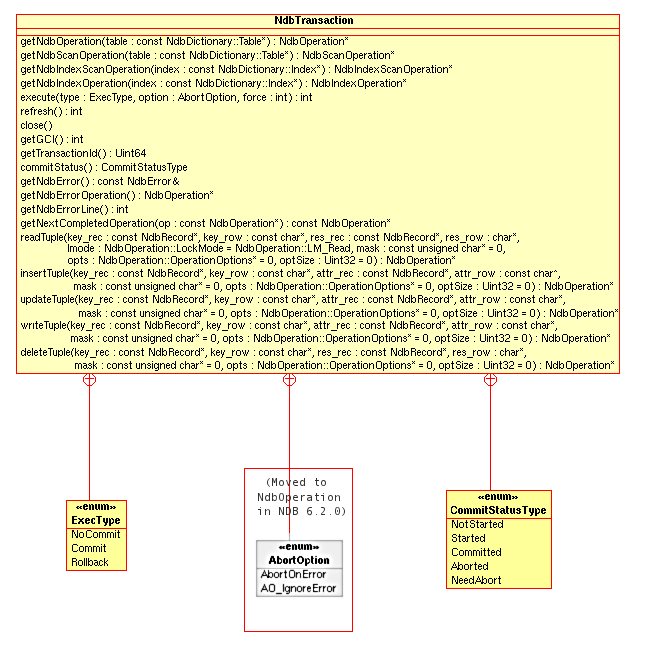
Class diagram.
This diagram shows all the available methods and enumerated types
of the ... class: